Nephrotic syndrome in a patient with Glycogen Storage Disease Type IXb.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51271/jpea-2022-192Keywords:
nephrotic syndromeAbstract
Introduction: Glycogen storage disorder (GSD) IXb is characterized by liver and muscle involvement. We present a GSD IXb patient with an incidental union of nephrotic syndrome.
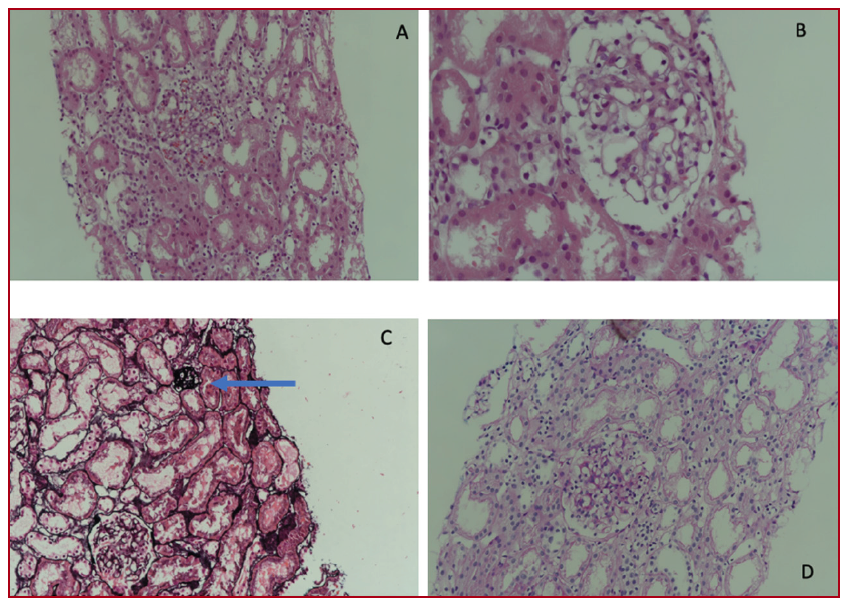
Case Report: A 4 year-old-patient was diagnosed with GSD IXb at 13 months of age with mildly elevated transaminases and hepatomegaly. During the follow-up period, there was no hypoglycemia. Development and growth were normal. In the last month, the onset of generalized edema was reported. Urinalysis showed a high protein level. He had low serum albumin, high serum triglycerides cholesterol. Complement levels were normal. The patient was diagnosed as minimal change disease with a renal biopsy. He was treated with oral prednisone.
Discussion: Minimal Change Disease is the most common cause of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome cases in children and the first step for therapy is the usage of corticosteroids. This is the first report of nephrotic syndrome associated with GSD IXb disease.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 The Journal of Pediatric Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.








