A Comparison of Leak Synchronized Nasal SIMV Methods and Leak Compensated Nasal SIMV in Newborns with Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Are Leak Synchronized or Leak Compensated Methods in Newborns with Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Keywords:
Prematurity, respiratory distress syndrome, surfactant, mechanical ventilation, leak compensation, leak synchronizationAbstract
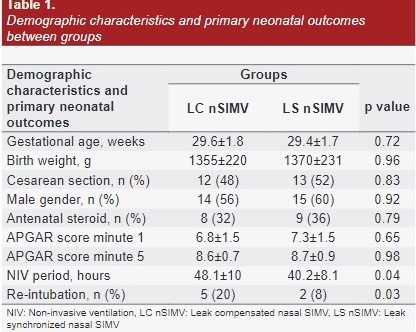
The aim of the present study was to compare the efficacy of leak compensated nasal SIMV (LCnSIMV) and leak synchronized nasal SIMV (LSnSIMV) modes in order to reduce the need for endotracheal intubation and associated complications in newborns with respiratory distress. This randomized, prospective study was conducted on 50 infants (25 per group) with gestational age below 34 weeks and/or below 2000 grams who have been admitted to NICU of Erciyes University Hospital because of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and need for mechanical ventilation. Infants with congenital heart disease, nasopharyngeal pathology (coanal atresia and cleft palate-lip) were excluded. Infants monitored on mechanical ventilator after surfactant were randomly assigned to LCnSIMV and LSnSIMV groups before extubation. SPO2/FiO2 (S/F), peak heart rate (PHR), respiration rate per minute (RRM), and arterial blood pressure (aBP) values of patients were recorded. Gestational age, birth weight, gender, RDS, patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) requiring treatment, presence of intraventricular bleeding (IVH), retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) were recorded. The patients enrolled in the study were female by 48% and male by 52%. There was not any statistically significant difference between groups for gender, postnatal age and birth weight. There was detected statistically significant difference between LCnSIMV and LSnSIMV groups for non-invasive ventilation period and re-intubation rate (p=0.04 and p=0.03, respectively). There was detected statistically significant difference between LCnSIMV and LSnSIMV groups for SpO2 and S/F rates at 60 minutes (p=0.03 and p=0.01, respectively). There was not any difference between groups for blood pressure, PDA, IVH, ROP, BPD, NEC, sepsis and air leak. It may be appropriate to prefer the LSnSIMV method in patients with respiratory distress syndrome who need non-invasive ventilation in the pre-extubation period by considering the patient-ventilator compliance for positive effect in terms of mechanical clinical variables.