The Antibiotic Usage Patterns in Pediatric Patients with Lower Respiratory Tract Infections at Quang Tri General Hospital, Central Vietnam
Antibiotics in Pediatric Lrtis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4274/jpea.2025.385Keywords:
Lower respiratory tract infections, pediatrics, antibioticsAbstract
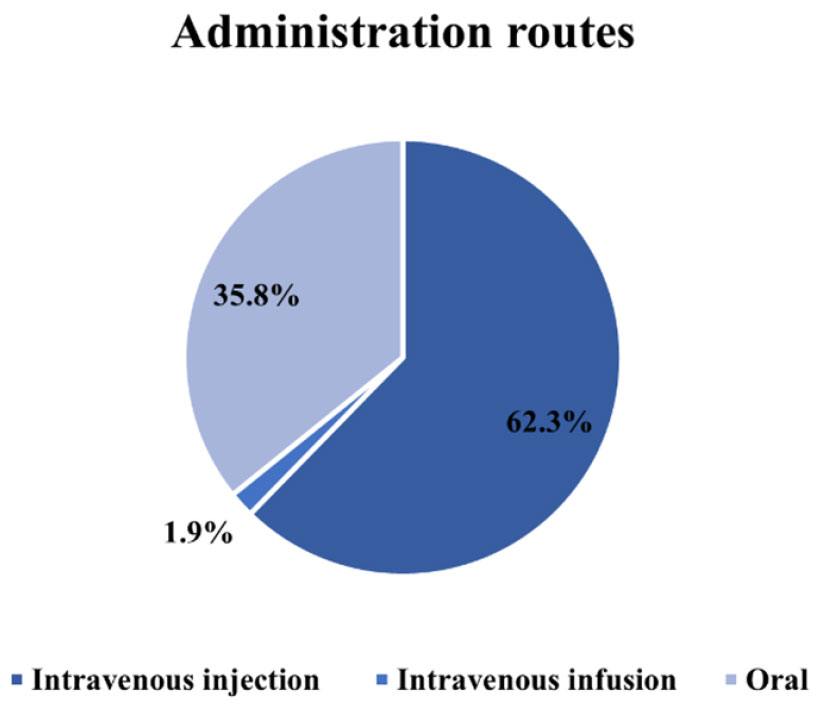
Lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI) are a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in children, especially in developing countries such as Vietnam. This study analyzed antibiotic use patterns in pediatric patients with LRTI at Quang Tri General Hospital in 2023. A cross-sectional design was used, examining 381 medical records of children aged 2 months to 5 years who received antibiotics for at least 3 days. Pneumonia was the most common diagnosis (82.4%), with severe illness observed in one-third of cases. The most commonly used antibiotic was cefotaxime (42.1%), mainly administered intravenously (62.3%). Antibiotic regimens varied, with an average of 1.55 drugs per patient. Most patients improved (99.0%) after treatment. The findings are consistent with existing literature on LRTI in children and provide insights into antimicrobial stewardship practices. This study highlights the importance of standardized protocols to optimize treatment and minimize inappropriate antibiotic use.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 The Journal of Pediatric Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.








