Acute Kidney Injury As A Consequence of Perinatal Asphyxia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4274/jpea.2025.364Keywords:
Acute kidney injury, hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, perinatal asphyxiaAbstract
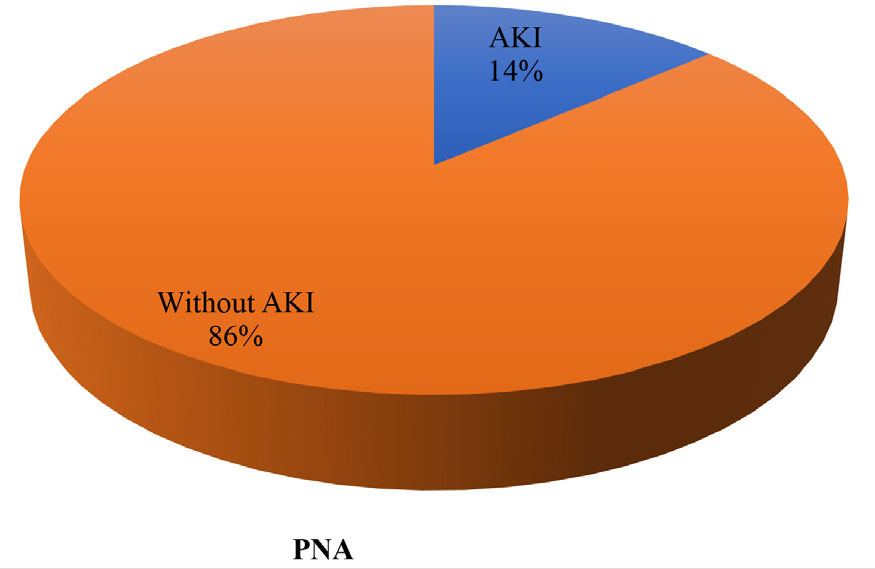
Perinatal asphyxia (PNA) results in multiorgan damage including the kidney. The severity of kidney damage is related to the extent of central nervous system damage. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of acute kidney injury (AKI) in neonates with PNA and its association with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) staging. This cross-sectional study was conducted in the neonatal intensive care unit of the Institute of Child and Mother Health, Dhaka, from July 2020 to June 2021. A total of 100 neonates with PNA were included in this study. After careful history taking, examination, and appropriate investigations, HIE staging was done in each subject using the Sarnat and Sarnat method. Data were analyzed by statistical package for the social sciences, version 23. In this study, 45 (45.0%) neonates belonged to the postnatal age group ≤24 hours, and male patients were predominant (57.0%). Out of 100 neonates, 89.0% had HIE stage II and 11.0% had stage III. Among stage II HIE neonates, 9 (10.1%) had AKI and 80 (89.9%) did not have AKI. Among stage III HIE neonates, 5 (45.5%) had AKI and 6 (54.5%) did not have AKI. The difference was statistically significant (p<0.05). When HIE stage was higher in PNA patients, there was a higher possibility of developing AKI. Renal function alterations correlated with HIE severity. Therefore, AKI should be evaluated and properly managed among neonates with PNA.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 The Journal of Pediatric Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.








