Hirschsprung Disease in a Female Infant: A Case Report
Hirschsprung Disease in a Female Infant
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4274/jpea.2024.337Keywords:
Hirschsprung disease, constipation, childrenAbstract
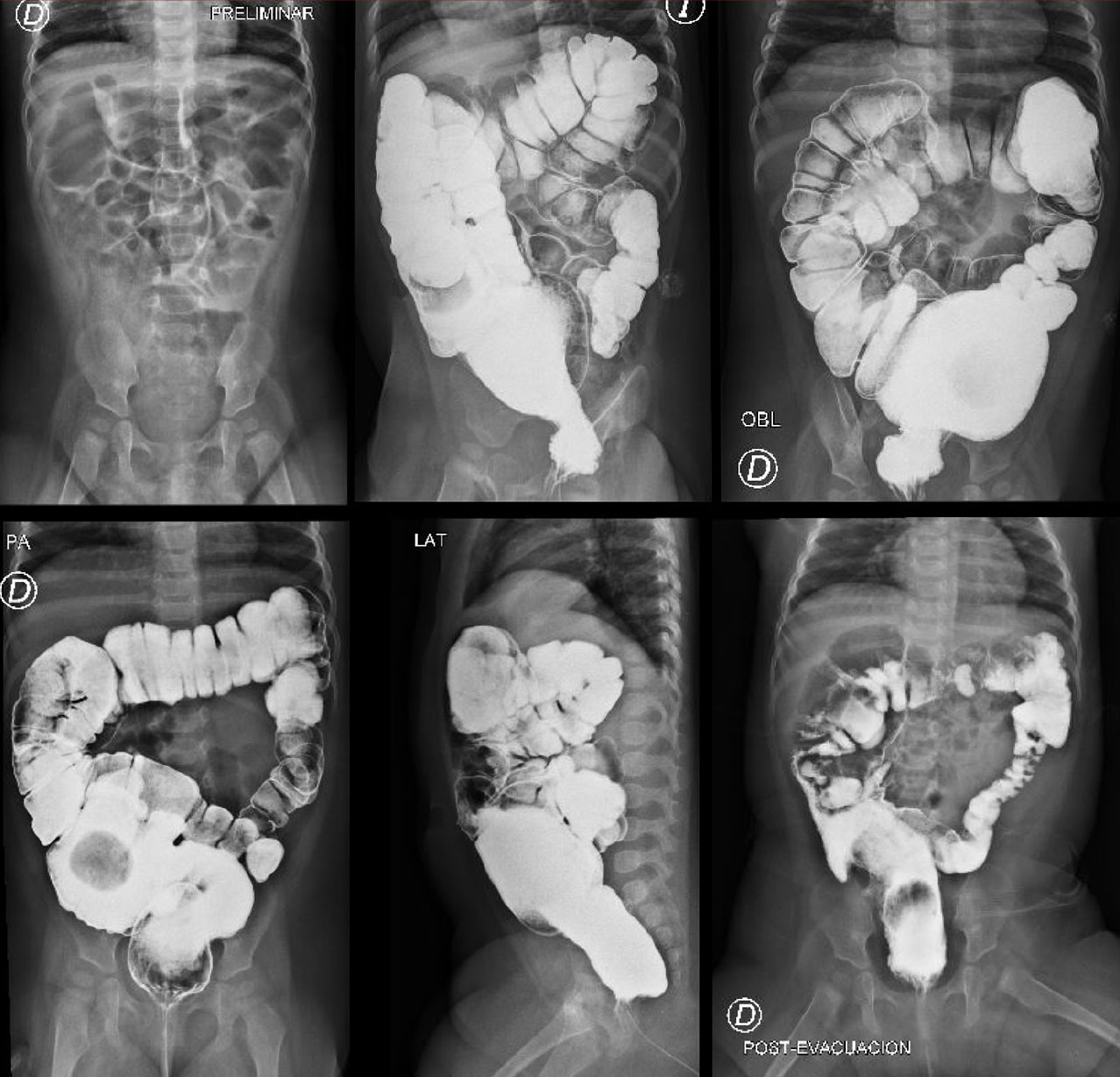
Hirschsprung’s disease (HD) is a congenital disease characterized by the absence of ganglion cells in the intestinal muscularis nerve plexus. The segment most affected was the rectosigmoid colon (80%). The clinical manifestations are non-specific; the common signs include vomiting, abdominal distention, and defecation alterations in early-life another feasible alteration is anemia. Anorectal manometry and contrast enemas are also highly useful. We present the case of a 9-month-old female with refractory constipation who was diagnosed with HD. Some theories explain that there is dysregulation of the microecological balance and intestinal mucosa. Imaging diagnostic methods are useful tools for screening HD. The mortality rate of these conditions is between 2% and 5%; therefore, a group of qualified professionals is necessary for treatment and postsurgical care.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Journal of Pediatric Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.








