Evaluation of Etiologic Agents of Lower Respiratory Tract Infections in Children Hospitalized Just Before Normalization of COVID-19
Agents of Lower Respiratory Tract Infections in Children
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4274/jpea.2024.255Keywords:
Children, etiologic agents, lower respiratory tract infections, real-time multiplex polymerase chain reaction test, virusesAbstract
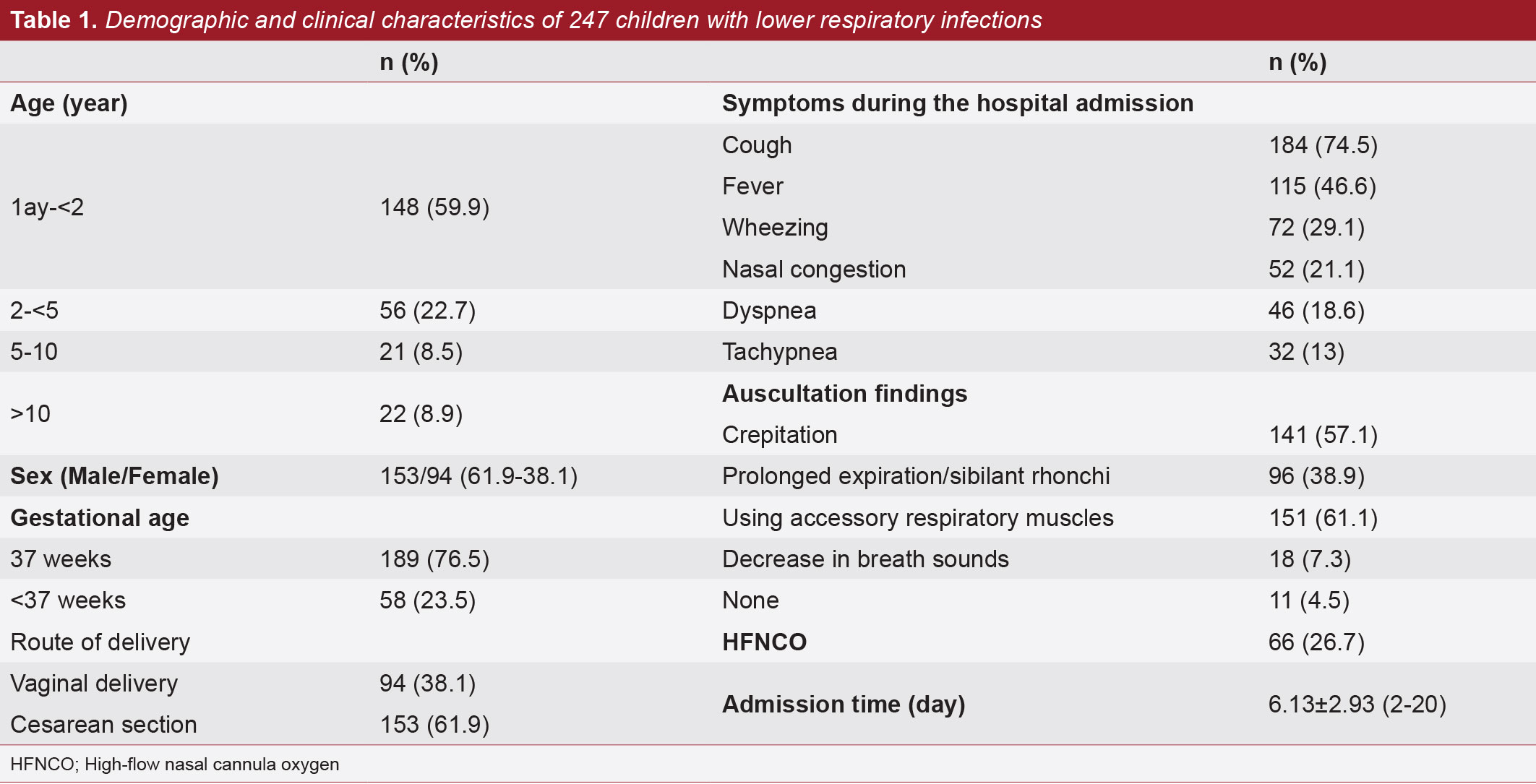
Lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) are one of the most common causes of hospitalization among children in the early childhood period. Knowing the pathogens that cause pneumonia, its management will be more exact and effective. In this study, we aimed to investigate the frequency of pathogens causing LRTIs in children at the end of the COVID-19 pandemic by performing a real-time multiplex polymerase chain reaction (RT-MPCR) test within our hospital. We included two hundred forty-seven children, aged between 1 month and 18 years, diagnosed with LRTIs, and hospitalized between May 2021 and April 2022. Demographic characteristics and clinical and laboratory findings were retrospectively collected from patients’ hospital records. Of the 247 children diagnosed with LRTIs, 153 (61.9%) were female. At least one pathogen was identified in the nasopharyngeal swap specimens of 218 (88.3%) patients, and 74.9% (n=185) of them were viruses. The most common identified pathogens were respiratory syncytial virus (24.7%), human bocavirus (21.1%), and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (15.4%). 7.7% of identified pathogens were bacteria. Haemophilus influenzae was the most commonly detected bacteria. Despite a lengthy period of isolating the community causative agents of pneumonia, their frequency remains unchanged from before the isolation time. RT-MPCR is beneficial for the early detection of pathogens and in the prevention of unnecessary antibiotic usage.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Journal of Pediatric Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.








