The Predictors of Pneumonia in Children with COVID-19
The Pneumonia in Children with COVID-19
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4274/jpea.2023.200Keywords:
Children with COVID-19, Pneumonia, Body mass index, Hematological parametersAbstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between the presence of pneumonia and blood parameters in cases
of Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and to examine their predictive characteristics in terms of pneumonia. We reviewed the file
records of 151 pediatric patients with a diagnosis of COVID-19 confirmed by the real time-reverse transcription polymerase chain
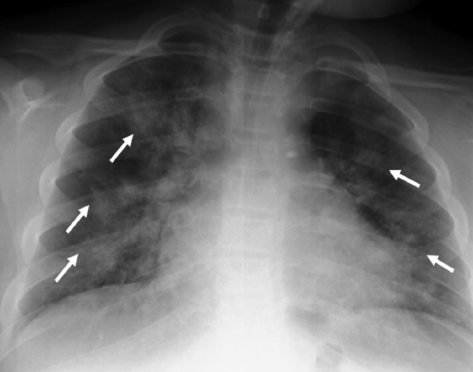
reaction test in nasopharyngeal swabs. The patients were divided into two groups based on direct chest X-ray and computed
tomography results in [Group 1 (n:41), with pneumonia findings, and Group 2 (n:110), with no pneumonia findings]. The groups’
demographic data, clinical and laboratory findings were compared. Pulmonary involvement was determined in 41 (27.1%) of
the 151 patients. The [body mass index (BMI) Z-score], red blood cell distribution width (RDW), mean platelet volume (MPV),
neutrophil lymphocyte ratio, passive leg raise, and D-dimer levels were significantly higher in patients with pneumonia than those
without pneumonia in our study. Based on multivariate logistic regression analysis, BMI Z-score, MPV, and RDW were found to
be independent risk factors of pneumonia in patients. The current study showed higher levels of blood parameters in patients with
coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID -19) presenting with pneumonia than those without pneumonia. We suggest that BMI-Z score
and MPV value may assist in predicting pulmonary involvement in patients with COVID-19.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 The Journal of Pediatric Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.








